Edge vs. Cloud Computing: What’s the Best Choice for Your Business?
🚀 The cloud revolutionized the way businesses store and process data, but now a new challenger has entered the ring—edge computing.
So, what’s the big debate?
- Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers.
- Edge computing brings processing closer to the data source, reducing latency.
💡 The question is: Should your business rely on cloud computing, move to edge computing, or use both?
This guide will break it down:
✅ What’s the difference between edge and cloud computing?
✅ Pros & cons of each approach
✅ Best use cases for different businesses
✅ How to decide which model fits your needs
By the end, you’ll know exactly which computing strategy will drive your business forward.
1. Cloud Computing: The Backbone of Digital Transformation
Cloud computing has been the go-to solution for businesses over the past decade. With platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, companies can scale computing resources on demand.
🔹 How Cloud Computing Works
Instead of running applications on local servers, cloud computing allows businesses to store and process data in remote data centers, accessed via the internet.
🔹 Example: A SaaS company like Slack hosts its platform in the cloud so users can access it from anywhere.
✅ Benefits of Cloud Computing
✔ Scalability: Scale up or down based on demand.
✔ Cost Efficiency: No need to invest in expensive on-premise infrastructure.
✔ Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere.
✔ Security & Compliance: Cloud providers offer built-in security measures.
❌ Limitations of Cloud Computing
❌ Latency Issues: Data must travel to centralized servers, which can cause delays.
❌ Bandwidth Dependency: Requires a stable internet connection.
❌ Data Privacy Risks: Sensitive data is stored on third-party servers.
🔹 Use Case: Cloud computing is perfect for SaaS companies, e-commerce platforms, and businesses needing scalable storage solutions.
2. Edge Computing: Bringing Data Processing Closer
Unlike cloud computing, edge computing processes data closer to the source—whether that’s a factory, a self-driving car, or an IoT device.
🔹 How Edge Computing Works
Instead of sending data to a remote cloud server, edge computing processes data on local devices or nearby servers, reducing latency.
🔹 Example: Tesla’s self-driving cars process real-time data on the vehicle itself rather than relying on the cloud.
✅ Benefits of Edge Computing
✔ Low Latency: Faster data processing for real-time applications.
✔ Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Less reliance on internet connections.
✔ Better Security & Privacy: Data stays closer to the source.
✔ Improved Reliability: Works even in remote areas with poor connectivity.
❌ Limitations of Edge Computing
❌ Higher Initial Costs: Requires investment in local infrastructure.
❌ Limited Scalability: Unlike cloud, scaling edge computing requires physical devices.
❌ Complex Management: Requires on-site maintenance and monitoring.
🔹 Use Case: Edge computing is ideal for smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT applications.
3. Edge vs. Cloud Computing: Key Differences
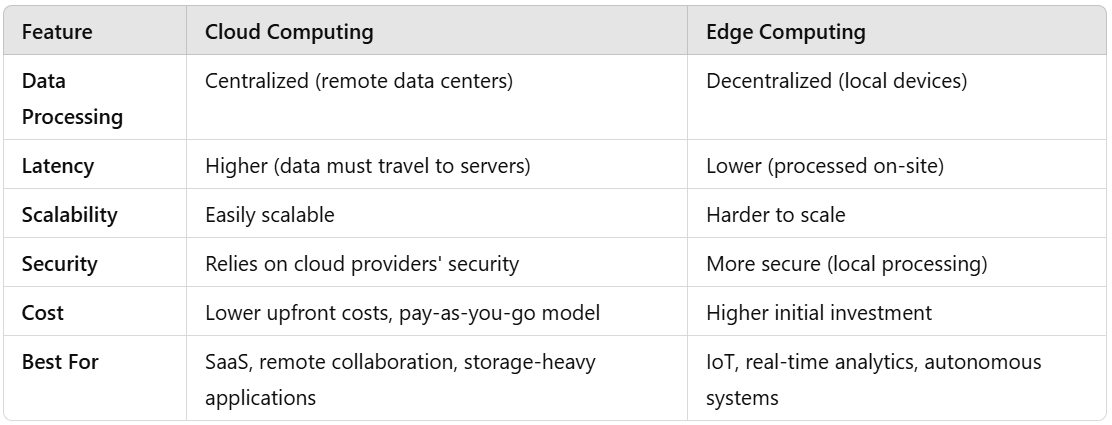
4. Which One Should Your Business Use?
🚀 The choice depends on your business needs.

🔹 Example: A healthcare provider using IoT-enabled medical devices can use edge computing for real-time patient monitoring but store data in the cloud for compliance and analytics.
5. The Rise of Hybrid Computing: Best of Both Worlds?
📌 What if you don’t have to choose? Many companies are adopting a hybrid approach—combining cloud and edge computing.
🔹 Example:
- Retail chains use edge computing for in-store checkout processing but rely on cloud computing for inventory management.
- Factories use edge computing for real-time equipment monitoring and cloud computing for predictive analytics.
💡 The Future: A mix of edge + cloud computing will dominate industries where speed, security, and scalability are essential.
6. FAQs (Optimized for Featured Snippets)
1. What is the key difference between edge and cloud computing?
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, while edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency.
2. Is edge computing better than cloud computing?
It depends on the use case. Edge computing is better for real-time applications, while cloud computing is better for scalability and storage.
3. Can businesses use both edge and cloud computing?
Yes! Many companies use a hybrid approach, leveraging edge computing for real-time processing and cloud computing for storage and analytics.
4. What industries benefit the most from edge computing?
Industries like healthcare, manufacturing, IoT, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles benefit from edge computing’s low latency and real-time capabilities.
5. How does edge computing improve security?
Since data is processed locally, edge computing reduces the risk of cyberattacks and keeps sensitive information out of third-party cloud providers’ hands.
🚀 Need expert developers for cloud or edge computing projects? → Hire Now
7. Final Thoughts: Making the Right Choice
The cloud vs. edge computing debate isn’t about picking one over the other—it’s about choosing what’s best for your business.
✔ Go Cloud: If you need scalability, cost efficiency, and remote accessibility.
✔ Go Edge: If you need real-time processing, better security, and offline functionality.
✔ Go Hybrid: If you want the best of both worlds.
💡 No matter what, you need the right tech talent to implement these solutions.
🚀 Need top-tier engineers for cloud or edge computing projects? Remoteplatz connects you with world-class developers.
🔗 Find elite engineers today → Hire Now
🚀 Ready to take your business to the next level? Remoteplatz has the best tech talent to power your cloud or edge computing strategy.
